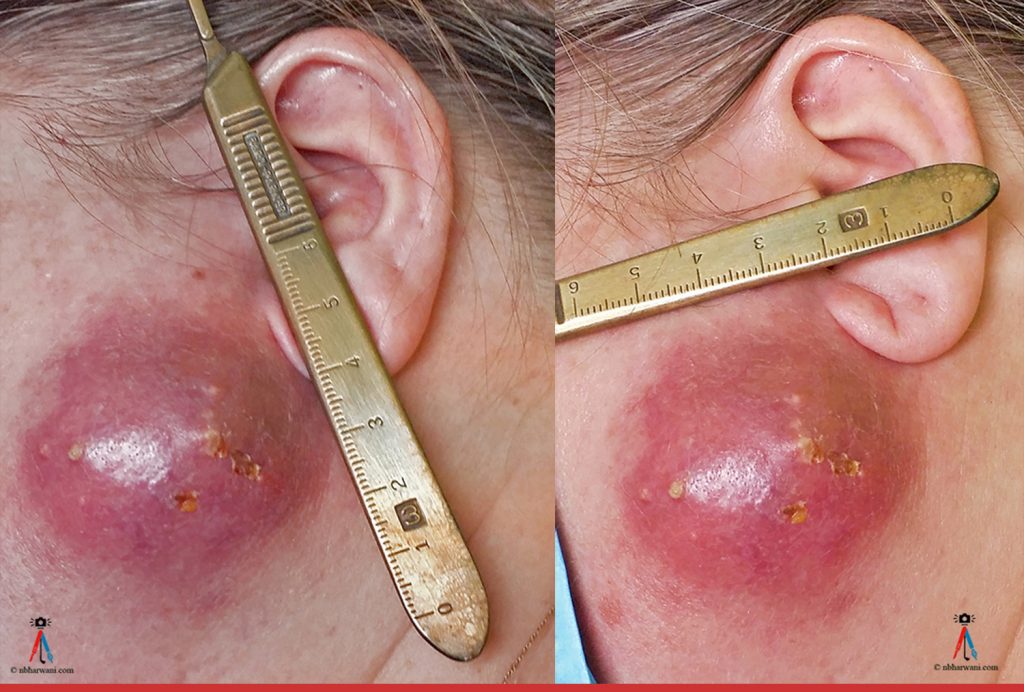
46 year-old female presented with a two-week history of an abscess over the left parotid area. The patient reports an abscess in the same location 18 months prior which she had aspirated. She has a medical history of Sjögren’s syndrome.
The patient had finished a course of amoxicillin-clavulanic acid and then was started on a course of a cephalosporin. Incision and drainage was done under local anesthetic and a large amount of pus was drained. The patient healed well.
Culture: Streptococcus anginosus
“Streptococcus anginosus is part of the human bacteria flora, but can cause diseases including brain and liver abscesses under certain circumstances.” (Wikipedia)
Pathology: Showed no parotid tissue. There was acute-on-chronic inflammation of subcutaneous tissues.
Salivary Gland
Infection: parotitis, sialandenitis
Symptoms – One-sided salivary gland swelling. Fever and pain will accompany the swelling.
Pathogens – Typically normal bacteria found in the mouth. Viral infections such as mumps often affect the salivary glands. Mumps most often involves parotid salivary gland. Mumps is a rare problem today because of the MMR vaccine.
Dehydration and malnutrition raise the risk of getting a bacterial infection.
Sjögren’s syndrome
This is a chronic autoimmune disease in which cells of a person’s immune system attack the salivary and other moisture-producing glands, leading to dry mouth and eyes. About half of people with Sjögren’s syndrome also have enlargement of the salivary glands on both sides of the mouth, which is usually painless.
Treatment
In some cases, no treatment is needed.
Antibiotics for fever or pus drainage, or if the infection is caused by bacteria. Antibiotics are not useful against viral infections.
Surgery or aspiration to drain abscess.
Self-care steps that can be done at home to help with recovery:
- Practice good oral hygiene. Brush teeth and floss well at least twice a day. This may help with healing and prevent infection from spreading.
- Rinse mouth with warm salt-water rinses (1/2 teaspoon of salt in 1 cup of water) to ease pain keep the mouth moist.
- Stop smoking.
- Drink lots of water and use sugar-free lemon drops to increase the flow of saliva and reduce swelling.
Prognosis
Most salivary gland infections go away on or are cured with treatment. Some infections will return. Complications are uncommon.
Complications
- Abscess of salivary gland
- Infection returns
- Spread of infection (cellulitis, Ludwig’s angina)
Prevention
In many cases, salivary gland infections cannot be prevented. Good oral hygiene may prevent some cases of bacterial infection.
Start reading the preview of my book A Doctor's Journey for free on Amazon. Available on Kindle for $2.99!
I see you don’t monetize nbharwani.com, don’t waste your traffic, you can earn extra cash every month with new monetization method.
This is the best adsense alternative for any type of website (they approve all sites), for more details simply search in gooogle: murgrabia’s tools