Now that the summer is fast approaching, we should revisit the topic of skin cancer. Today, we will discuss melanoma, next week we will visit non-melanoma skin cancers and in the third week we will discuss appropriate use of sunscreen.
In early stages, surgical removal of melanoma is usually successful. Once the melanoma has spread then the prognosis is grim. Recently, FDA has approved certain drugs to be used in late stage melanoma. But these drugs do not cure the cancer and the side-effects are many. The current prognosis for survival in metastatic melanoma is nine months or less, with 9,000 people dying in the U.S. each year.
For Canadian males, the rate for melanoma has tripled since the late 1960s. For Canadian females, the rates have varied over the years but still show a gradual increase. The death rate from melanoma continues to rise about two percent annually. Approximately, two per cent of melanomas occur in patients under the age of 20 years, and about 0.4 per cent of melanomas occur in pre-pubertal children.
Melanoma arises from cells called melanocytes. These cells contain melanin (melas = black) – a principal pigment responsible for the color of human skin, hair, and eyes. Melanin also acts as a filter to decrease the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays to the dermis.
When the skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation, there is immediate increase in the number of melanocytes and production of melanin pigment. This results in tanning. The amount of melanin produced is genetically determined. That is why some people burn easily without tanning.
The risk of skin cancer is increased in individuals who spend too much time outdoors; children who have had episodic sunburn, and if there is a family or personal history of skin cancer (especially melanoma). Males are affected more than females.
Melanoma is usually found on the backs or chest in men and lower legs in women. These areas are most exposed to sunlight. Melanoma can also occur in eyes, mouth or internal organs although these areas are not directly exposed to sun.
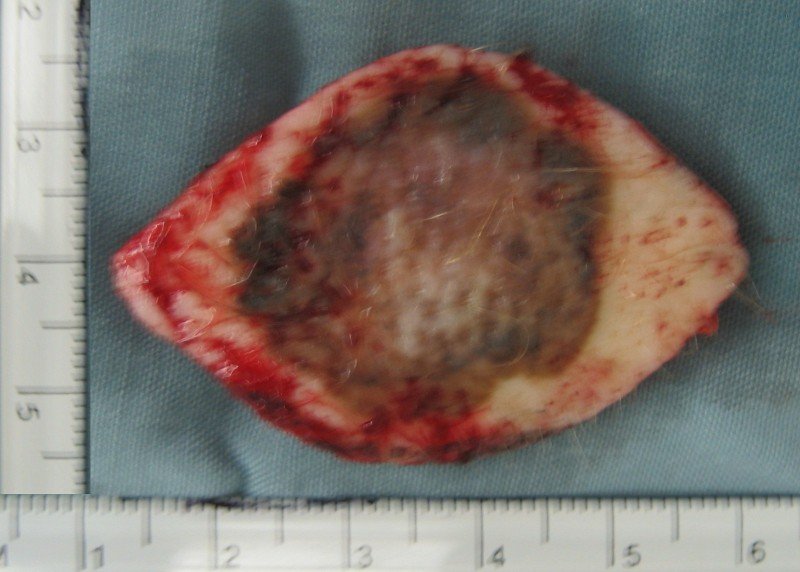
Examples of melanoma on the abdominal wall skin: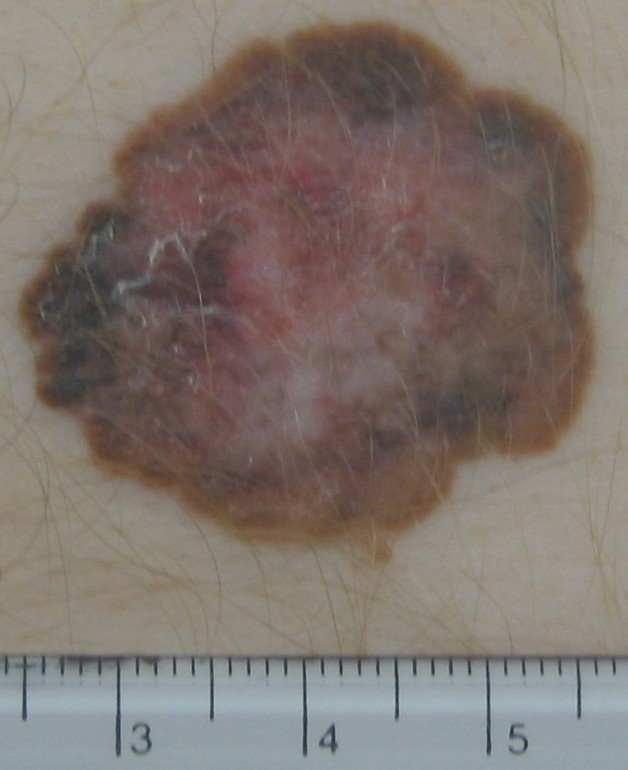
There are four different types of melanomas:
-superficial spreading melanoma: most common, looks like a spreading mole
-nodular melanoma: 10 per cent of cases, looks like a dome rising from a mole
-lentigo maligna: less common, looks like an irregular stain in older Caucasians, not related to moles
-acral lentiginous melanoma: found in all skin types in the sole of the feet, palms of the hands, undersides of the fingers or finger nails or toe nails
Prevention is better than cure. We should avoid sunburn and generally reduce exposure to ultraviolet radiation by staying out of the midday sun, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade and applying sunscreen.
Now, that cannot be too difficult!
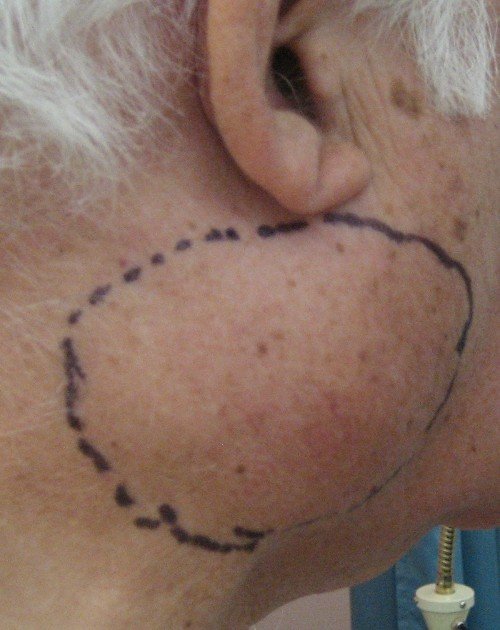
Example of recurrent melanoma: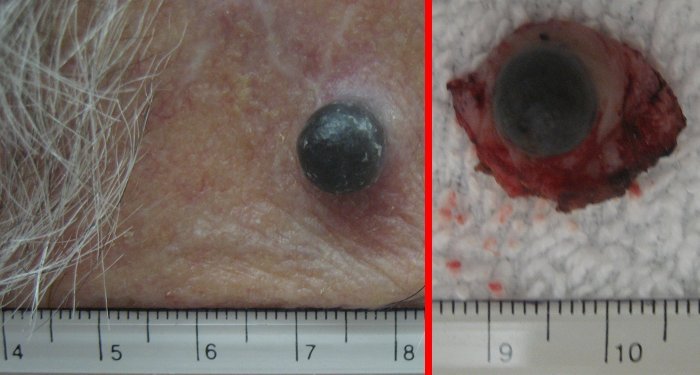
Start reading the preview of my book A Doctor's Journey for free on Amazon. Available on Kindle for $2.99!